Two Sides to the Forecasted Telecom Spending Increase
IDC Telecom Services Tracker Finds Accelerated Telecom Services Growth Due to ????
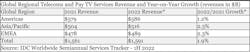
Worldwide spending on telecommunications and pay TV services will be nearly $1.6 trillion in 2022, representing a year-over-year increase of 1.9%, according to the International Data Corporation (IDC) Worldwide Semiannual Telecom Services Tracker. The latest forecast is a bit more optimistic than the version published in May as it assumes growth in total market value will be 0.5 percentage points higher. IDC believes that this positive movement is a consequence of inflation (i.e., the increase in tariffs for telecommunication services).
“…inflation is here to stay for at least the next three years. Consequently, the dance between increasing prices and decreasing demand will remain one of the main stories in the telecom industry. Although the elasticity of telecom services is relatively low, inflation, together with a possible recession, might ruin the fragile balance between prices and demand.”
As a result of the inflationary pressures that have begun to threaten their profitability, telecom operators have recently increased the tariffs for their services. A simple analogy indicates that the higher tariffs mean clients are paying more, and the total nominal value of the market is growing faster than previously expected. This trend is common across all global regions and has caused similar changes in their respective revenue forecasts for 2022:
- Growth in the Americas increased by 0.3 percentage points.
- Growth in Asia/Pacific increased by 0.5 percentage points.
- Growth in EMEA increased by 0.9 percentage points. The increase in EMEA comes mostly from Europe, a region that is witnessing higher-than-average inflation while struggling to find a replacement for cheap Russian energy. Still, the fastest revenue growth this year is expected in the Asia/Pacific region, driven by the relatively lower saturation of the telco markets in less-developed countries. (See Figure 1.)
With the tariff increases, most operators have initially focused on the mobile section of the market, lifting the average prices by a high-single-digit percentage. This is because the mobile section represents a major part of every telco market, so the outcome of such action is visible sooner. In the fixed segment, and especially in its B2B portion, there is typically a high proportion of customers with multi-year contracts that cannot be broken without penalties. Consequently, the forecast for mobile services spending in 2022 has increased by 0.7 percentage points, above the average for the overall market.
Inflation does not bring only a positive boost to the market. On its flip side, it generates a deterioration of the purchasing power of consumers and businesses, thus causing a decrease in demand. Fortunately, in the case of telecom services, the decrease in demand is not likely to be massive. This is because the elasticity of telecom services, just as of any other utility services, is relatively low (i.e., the demand for such services changes less than proportionally when its price increases or decreases). Elasticity is higher in less developed countries simply because a bigger share of clients is not able to afford more expensive services—they usually opt to migrate to cheaper packages or even drop some services that they consider replaceable. In contrast, the elasticity is lower in countries or regions with higher purchasing power—and that explains the relatively higher boost of spending in Europe as mentioned above.
“Fortunately, in the case of telecom services, the decrease in demand is not likely to be massive. This is because the elasticity of telecom services, just as of any other utility services, is relatively low (i.e., the demand for such services changes less than proportionally when its price increases or decreases).”
According to the latest forecasts published by the International Monetary Fund, inflation is here to stay for at least the next three years. Consequently, the dance between increasing prices and decreasing demand will remain one of the main stories in the telecom industry. Although the elasticity of telecom services is relatively low, inflation, together with a possible recession, might ruin the fragile balance between prices and demand. "This puts telecom operators in an uncomfortable position," said Kresimir Alic, Research Director, Worldwide Telecom Services at IDC. "Maintaining healthy margins will require additional rounds of price increases, and their ability to carefully balance between the two forces will determine the future development of telco markets in individual countries, regions, and the whole world."
Source: IDC Tracker
For more information about IDC's Worldwide Semiannual Telecom Services Tracker, please contact Kathy Nagamine at 650-350-6423 or [email protected].